Predictive Maintenance
Everything you need to know about predictive maintenance
What is predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance in short, is a technique that uses data analysis tools to detect anomalies in your data, helping to prevent costly errors in your equipment and processes. You could actually save a lot of money by being able to predict when, for example, a machine is about to break down, rather than only noticing when the machine has broken down.
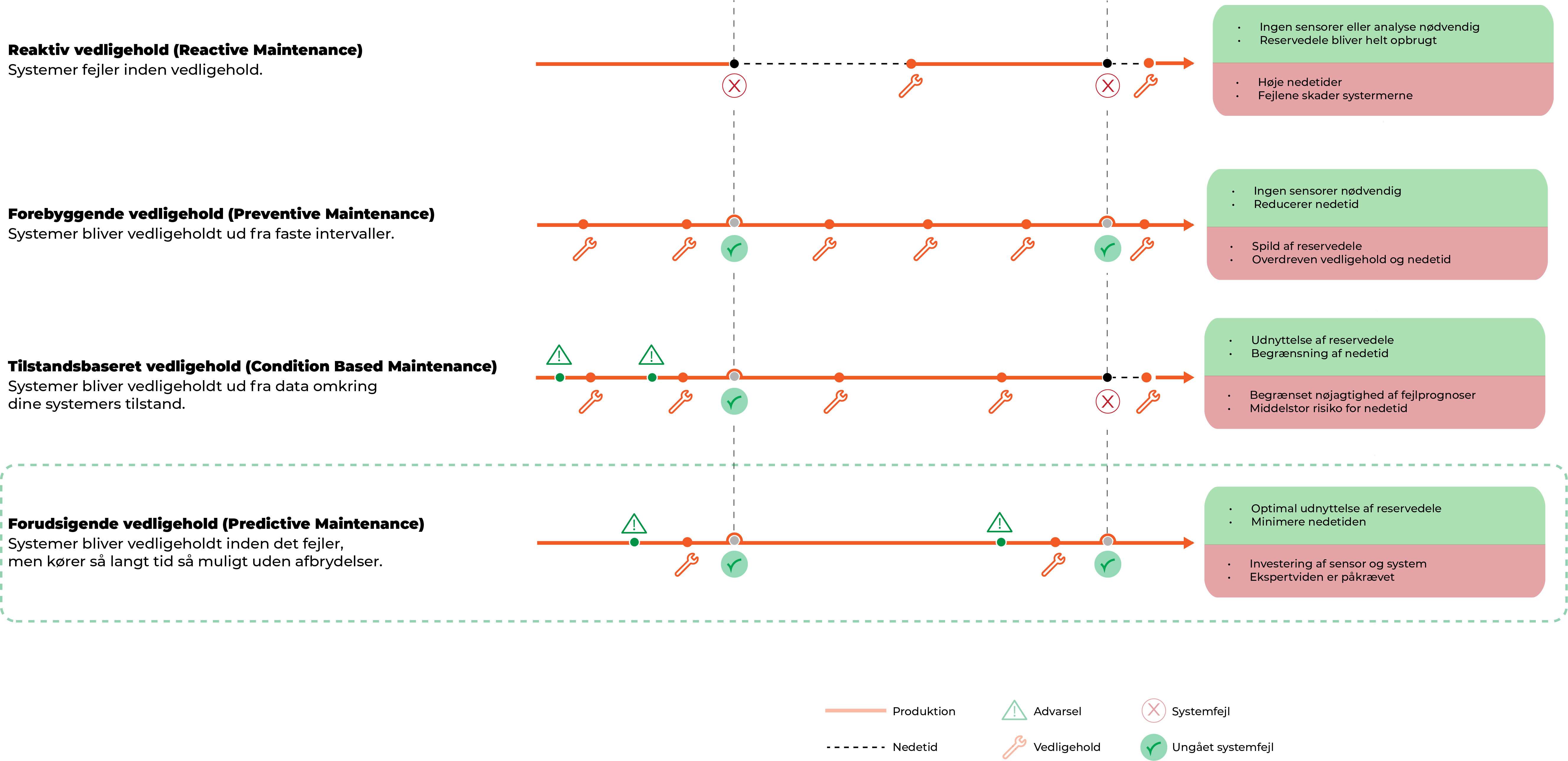
Hvis vi hopper et skridt ned i hvordan man kan forstå predictive maintenance, kan man sammenligne det med tre former for vedligeholdelse, som ses i en industriel kontekst; reaktiv -, forebyggende – og tilstandsbaseret vedligeholdelse.
Reactive maintenance refers to repairs carried out when the equipment has already failed, in order to bring the equipment back to normal operating condition. If you use reactive maintenance in a production, neither sensors nor digital systems capable of monitoring your equipment are needed and you are sure that spare parts are used up. The consequence of reactive maintenance is that there will be prolonged downtime and the failures that occur can potentially damage systems.
Preventive maintenance is carried out regularly and routinely on your equipment and machinery to reduce the risk of equipment failure and unplanned downtime. Again, sensors are not required and unplanned downtime is reduced. However, by applying preventive maintenance in your production, there will be an excessive consumption of both spare parts and time spent on maintenance.
Condition-based maintenance is a strategy where you monitor the actual condition of your machines/systems to determine what maintenance should be performed. This strategy dictates that maintenance should only be performed when certain indicators show signs of declining performance or upcoming failure. This means you can optimize the use of your spare parts while limiting downtime. With this type of maintenance, you may find that the indicators do not predict a failure unless they are set up correctly according to what you want to monitor, thus there is still a risk of failure prediction and therefore unwanted downtime.
How does predictive maintenance work?
Predictive maintenance uses historical and real-time data from different parts of your operation to anticipate potential problems before they affect your operations.
Det første skridt er at fastlægge baselineværdier. Du skal overvåge en maskines betingede basislinje og indsamle data, før du installerer sensorer. På den måde er der, når du begynder at indsamle betingede data, noget som du kan betragte som “normale og velfungerende datasæt”. Disse datasæt bruges i sammenligningen af alt nyt data, hvor noget kan risikere at stikke udenfor. Derfra er det enkelt – hver gang maskinen fungerer uden for de normale parametre og datasæt, udløser sensorerne din protokol for predictive maintenance. Når det sker, vil du altså få af vide, når du aktivt skal reagere på noget.
Benefits of predictive maintenance
With predictive maintenance, machines are serviced only when necessary. That is, just before failures are likely to occur. This leads to more cost savings:
- Reduction of equipment maintenance time
- Reduction of production hours lost due to maintenance
- Reduction of costs for spare parts and supplies
That's a big advantage - studies show that unplanned downtime costs industrial manufacturers about $50 billion each year!
In addition, predictive maintenance can be used to facilitate logistics by maintaining machines at convenient times - for example, outside production hours or while the necessary personnel are nearby. Finally, it can also help purchasing departments by predicting which spare parts will be needed at what time.

Figures from Deloitte Analytics Institute report
The 5 steps to implement predictive maintenance
1. The management makes a decision:
In most instances, the case is presented to management before predictive maintenance is implemented on the factory floor. Then the machine operators and maintenance staff are trained to use the new technology and then the actual implementation begins.
2. Establish baselines
The maintenance team establishes acceptable baseline values for the assets that are to have sensors installed.
3. Installation of Internet of Things (IoT)-devices:
The IoT sensors are installed on the critical equipment of the system. This may include a vibration meter mounted on a mechanical component of the system.
4. Configuration and development of IoT system and dashboard:
The IoT devices must be connected to an IoT system where data is collected, processed, analyzed, and ultimately visualized in a dashboard.
5. Predictive maintenance in operation:
Inspections can now be planned automatically when baseline values are exceeded, and machine operators and maintenance personnel can maintain their production based on a database foundation.