5G and IoT
Regardless of whether you are an advocate, opponent, or have yet to fully grasp the concept, it cannot be ignored - 5G has arrived and is here to stay.
But what exactly is 5G, and why is it controversial in many parts of the world, and what does it have to do with the Internet of Things? You will find the answers in this post.
Happy reading!

Time to read: 17 minutes
Subject: 5G, Development, Networks, Data, Technology
Author: Iterator IT
What is 5G?
5G is an abbreviation for 5th generation mobile network – also known as 5G NR (New Radio) or simply the next generation mobile network. With 5G comes the promise of a faster, more stable, and more secure network. In addition, the new network technology also provides greater capacity and less response time for data transmission. We will delve more into this later in this blog post.
As we become more and more digital in our personal and professional lives, it is natural that the internet must evolve and keep up with the demand for more efficient online activity. That is why 5G has been introduced. The many promises of a better and faster network create the opportunity for better development and utilization of new technologies such as automation, robotics, VR, AR, and, of course, IoT.
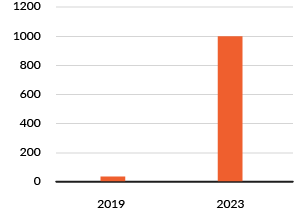
According to IDC , there were around 10 million wireless 5G connections in the world in December 2019. It is estimated that this number will rise to around 1 billion connections in 2023.
This is an increase of no less than 217 % per year.

From 1G to 5G
You may not be aware of it, but actually, 1G - our first mobile network - already saw the light of day in the 1980s. 1G made it possible for us to call Swedish, Norwegian, and Finnish phone numbers at the same rate as a Danish phone number. However, it was still expensive to call, and a mobile phone typically weighed 6-8 kg and was therefore not common.
About 10 years later, 2G was introduced to the world. Among other things, this meant that we could get unique numbers through sim cards that were no longer attached to the phones. Mobile phones could suddenly be made so small that they could fit in a pocket. The special thing about 2G, however, was that we could now also write to each other using SMS messages.
3G was introduced in 2003 as a solution to the increasing internet usage, which was only exacerbated by the introduction of the first smartphones in the same decade. 3G could handle both data and voice, and the network had a much faster connection than before. This provided new possibilities, such as browsing and streaming music and movies on the phone, as well as the ability to receive emails and use social media.
4G (also called 4G LTE for Long Term Evolution) was introduced in Denmark in 2011 and is still used to this day. The 4G network connection is so fast that it is also possible to use mobile broadband via a 4G modem or a 4G router. Additionally, 4G was also revolutionary for our phone calls, as the fast network meant we could be connected in 1 second instead of 10 seconds, as was the case with 3G.
But the most fascinating thing about the 4G network was that it enabled the development of what we now know as the Internet of Things. With the introduction of 4G, it became possible to get machines and other devices to communicate over the network.
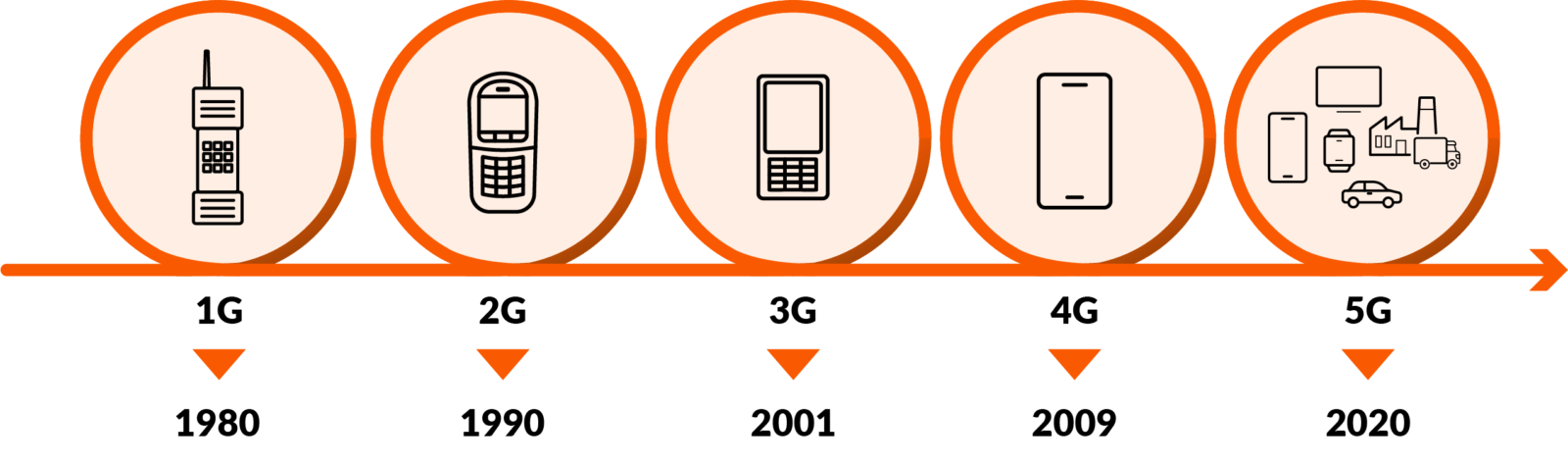
5G is a further development of the 4th generation mobile network (4G LTE). The new network is designed to handle the increase in the number of devices connected to the Internet that is happening worldwide. In broad terms, 5G differs from 4G by having greater capacity, increased upload and download speed, and shorter response time.
The vast majority of private individuals and businesses still use the 4G network, but there is relatively broad agreement that the 5G network will have a significant impact on many aspects of our lives, including having a massive impact on the possibilities with IoT.
What does 5G IoT mean?
There is no doubt that the average person will benefit from the network in the form of more opportunities for smart devices in the home and faster download of their favorite shows. The big winners, however, are to be found in industry. Higher capacity, increased speed, lower latency, and more reliability and stability all contribute to making IoT in industry - and among companies in general - far more attractive.
But why is 5G so important for IoT development? This is largely due to the low latency.
The success of an IoT project usually depends on the performance of the devices. That is, how quickly the IoT device can communicate with other IoT devices, smartphones, tablets, or other software such as apps and websites. 5G provides the opportunity to make this communication much faster.
When we talk about low latency, the self-driving car is a classic example. If the car's reaction time is not fast enough to detect changes in traffic such as hard braking, it will never be a success. Many believe that the 5G network will be the mother of the self-driving car. The same applies in many other industries. Take, for example, the surgeon who has to operate remotely on a patient using robotic arms. In that situation, it is literally vital that the robotic arms respond instantaneously.
In addition to the low latency, it is also worth mentioning the 5G network's more stable connections, which benefit those who use IoT. The promise of stable and reliable connections creates even more opportunities for security in the form of smart locks, cameras, and other real-time surveillance equipment for both individuals and businesses.
In addition, 5G's increased capacity means that many more devices can be connected to the same network.
However, to take advantage of all the many opportunities with 5G, it naturally requires an investment in 5G-compatible IoT devices. And even though the new network promises a bucketful of gold for those who invest in 5G IoT, it is still a new field that requires testing and competent developers who know what it takes to achieve 5G's full potential for IoT projects.
How does 5G work?

The many promises of faster connections, low latency, greater capacity, and more are not just about 5G being a "new version" of the 4G network. The new network differs in many ways from the previous networks, using new frequency ranges, for example.
In Denmark, we are divided into what the telecommunications companies call cells hat is, geographical areas where antennas are placed on masts or tall buildings. Within such a cell, the network uses so-called radio frequencies, which ensure that the antennas do not interfere with each other and provide weaker signal strength to consumers.
Each cell has a signal that the antennas send to internet-connected devices such as smartphones, routers, tablets, and more. They are sent in the form of radio waves within a certain radius. The connected devices also send radio frequencies back to the antennas.
Okay, it may be a bit complicated. But hold on, because now we come to where 5G differs from the other networks.
With 2G, 3G, and 4G, these radio waves are broadcast widely from the antenna, and this is where 5G differs significantly. 5G antennas use "beamforming" which means that 5G sends directional beams to individual devices instead of "shooting with a scattergun." This means, among other things, much better signal strength since radio waves cannot interfere with each other. At the same time, this technology is also much more efficient than before, and less mobile radiation is emitted.
It's a win-win-win.
In addition to using new frequency ranges and directional beams, it is also planned to deploy more and smaller antennas than with the 4G network. This enables so-called network slicing. This means that certain 5G networks can be divided into several networks that operate independently of each other. Such a network is private and is not shared with others, which means increased control, better security, and stability.
Advantages of 5G
Whether you are a supporter of the new 5G network or not, there are undoubtedly many advantages to be gained. Some of those we have highlighted in this post are:





More capacity
Increased speed
Better latency
More efficient energy consumption
Increased security
With the 5G connection, it becomes possible to up and download files much faster than before. This is both an advantage when you, as a private individual, stream, play or send large files. But it will also significantly affect companies that need to collect, analyze, and structure large amounts of data. The increased response time is also ideal for companies where IoT is not only used to collect data but also to initiate actions through communication from one device to another. Again, the self-driving car is an excellent example of this advantage.
Next, it is worth mentioning that the consumption of IoT devices by Danes has increased significantly in recent years, and this trend is expected to continue. With the 5G connection, our network will have the opportunity to keep up with the increasing use of smart devices in homes and Danish workplaces. However, with the growing use of IoT devices, it is important not to forget security. With increased digital behavior, we unfortunately see a significant increase in digital crime. The 5G network promises opportunities for higher security and stability when installed and used correctly.
Finally, the network is said to deliver data traffic with much lower energy consumption than was the case with the 4G network. Another advantage in a world where the green transition is high on the agenda.

When will 5G come to Denmark?
At the end of 2020, the 5G network was opened in a few places in Denmark, mainly in Copenhagen. However, several network providers promise to roll out the network to the rest of Denmark during 2021.
If you want to know more about 5G in Denmark, you can advantageously read the Energy Agency's 5G action plan for Denmark.
Why do some people believe that 5G is dangerous?
The question of whether 5G is dangerous is still being heavily debated. There are people who believe and fear that 5G radiation can be harmful to humans, animals, and the environment. It is particularly the increased frequencies that create uncertainty and concern.
Some of the concerns that have been circulated are that 5G radiation causes brain cancer. However, studies from Sweden, Finland, and England show that 5G radiation is more than 200 times lower than the limit values that Denmark follows (source: DR News, February 2020).
At the Danish Health Authority the assesment are that there is no reason to be concerned about health risks associated with 5G, as the radiation is so weak. The same goes for the worldwide organization WHO – World Health Organisation.
Do you want to join the 5G IoT wave?
If you are left with a vision that IoT can be the way forward for you now and when the new 5G network is rolled out, and would like to know more about your options for IoT already today?
Then you are very welcome to contact us here - and we will have a non-binding dialogue about your options.
Iterator IT
Iterator IT is one of Denmark's leading IoT development companies, specializing in Industry 4.0. We are well-versed in the complex business models that exist in the industry. Over the years, we have assisted industrial companies in developing their Industry 4.0 projects, not just in terms of software development, but also by examining the various elements of the company from the ground up until we find a concrete use case that can create value for the company. In some cases, we have also been the primary driving force that has brought the project to fruition in collaboration with a project manager within the company.
We build the software for the project, including the cloud solution and visual elements for platforms or applications. With our skilled and experienced collaborators who have developed hardware over the years, we are capable of offering end-to-end IoT solutions.
If you have any doubts about what Industry 4.0 can do for you, please feel free to contact us either via our contact form here or call our CEO Casper at +45 31 39 05 69
